


30% Energy Efficient Motors
JianTai equips its plastic extrusion machines with motors that are 30% more energy efficient. These advanced motors significantly reduce energy consumption, lower operational costs, and enhance production sustainability. By choosing JianTai, you gain high-performance machinery and contribute to a greener environment. Invest in energy efficiency and reliability with JianTai’s state-of-the-art extrusion solutions.
Extrusion Screws for Longer Life
JianTai designs plastic extrusion machines with specially crafted screws that ensure longer life and superior performance. We use high-quality materials and engineer these screws for durability, reducing wear and maintenance needs. By choosing JianTai, you invest in reliable, long-lasting equipment that enhances production efficiency and minimizes downtime. Enjoy the benefits of extended operational life and consistent output with JianTai’s advanced extrusion technology.

Read more about Plastic Extrusion Machine
Comprehensive Guide to Plastic Extrusion Machine
Plastic extrusion machines play a crucial role in manufacturing a wide variety of plastic products. These machines melt raw plastic material and form it into a continuous profile. Manufacturers commonly produce pipes, tubes, window frames, and plastic sheeting through plastic extrusion. In this guide, we will explore plastic extrusion machines, their components, operation, types, applications, and maintenance.
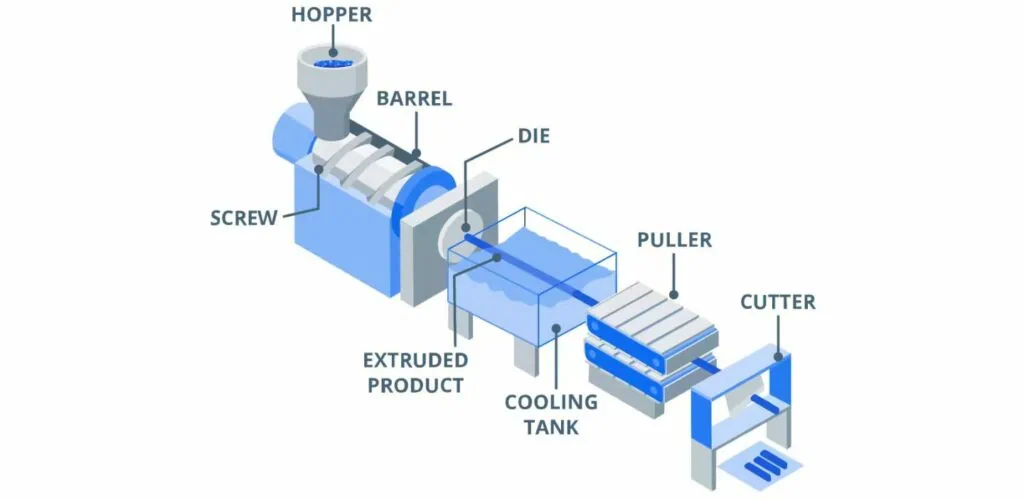
Components of a Plastic Extrusion Machine
A typical plastic extrusion machine includes several key components:
- Hopper: You start the extrusion process by loading raw plastic material into the hopper. The hopper holds the raw plastic material, usually in the form of pellets or granules.
- Extruder Barrel: The raw plastic material heats and melts in the extruder barrel. Heaters in the barrel ensure the material reaches the desired temperature.
- Screw: Inside the barrel, the screw rotates to push the molten plastic material forward through the barrel.
- Die: Attached to the end of the barrel, the die shapes the molten plastic into the desired profile as it exits the extruder.
- Cooling System: Once you shape the plastic, you must cool it to solidify. Typically, you achieve this using water baths or air cooling systems.
- Puller: The puller pulls the extruded plastic away from the die at a controlled rate.
- Cutter: In the final stage of the process, you cut the continuous plastic profile into the desired lengths.
Operation of a Plastic Extrusion Machine
Operating a plastic extrusion machine involves several steps:
- Feeding: You begin by feeding raw plastic material into the hopper.
- Melting: As the material moves along the barrel, the rotating screw conveys it while heating it to its melting point.
- Shaping: The molten plastic is then pushed through the die, shaping it into the desired profile.
- Cooling: Immediately after shaping, you must cool the plastic to prevent deformation.
- Pulling and Cutting: Finally, the cooled plastic profile is pulled away from the die and cut to the required lengths.
Types of Plastic Extrusion Machines
Plastic extrusion machines come in various types based on their specific applications:
- Single Screw Extruders: These are the most common and handle simple extrusion tasks. They are ideal for processes involving only one type of plastic.
- Twin Screw Extruders: For more complex processes, such as compounding, twin screw extruders are used. They offer better mixing and more consistent output.
- Sheet Extruders: These machines are designed specifically for producing plastic sheets, utilizing flat dies to create wide, thin profiles.
- Pipe Extruders: To make pipes and tubes, manufacturers use pipe extruders with circular dies and additional cooling systems to maintain the shape of the cylindrical profile.
- Profile Extruders: These machines produce complex shapes and profiles, such as window frames and other custom-designed extrusions.
Applications of Plastic Extrusion
Plastic extrusion finds applications in various industries due to its versatility and efficiency. Some common applications include:
- Construction: You can produce pipes, window frames, and insulation materials.
- Packaging: Plastic films and sheets for packaging products are made using extrusion.
- Automotive: Various plastic components in vehicles, such as dashboards and trim, are extruded.
- Consumer Goods: Items like plastic toys, containers, and household goods often undergo extrusion.
- Medical: Tubing and other plastic components used in medical devices are produced through this process.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
To ensure optimal performance and longevity of plastic extrusion machines, regular maintenance is crucial. Key maintenance practices include:
- Regular Cleaning: Keeping the hopper, barrel, and die clean prevents contamination and blockages.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication of all moving parts, especially the screw, reduces wear and tear.
- Inspection: Regularly inspecting heaters, screws, and dies helps detect signs of damage or wear.
- Calibration: Periodically calibrating the machine maintains accuracy in the extrusion process.
When troubleshooting, you may encounter some common issues:
- Inconsistent Output: This could be due to variations in material feed or improper temperature settings.
- Poor Surface Finish: Die contamination or improper cooling rates often cause this issue.
- Excessive Wear: Regularly inspecting and replacing worn parts can prevent this problem.
Conclusion
Plastic extrusion machines are essential for producing a wide range of plastic products. By understanding their components, operation, types, and maintenance requirements, you can optimize their performance. With regular maintenance and troubleshooting, these machines will consistently deliver high-quality output, making them indispensable in various industries.

